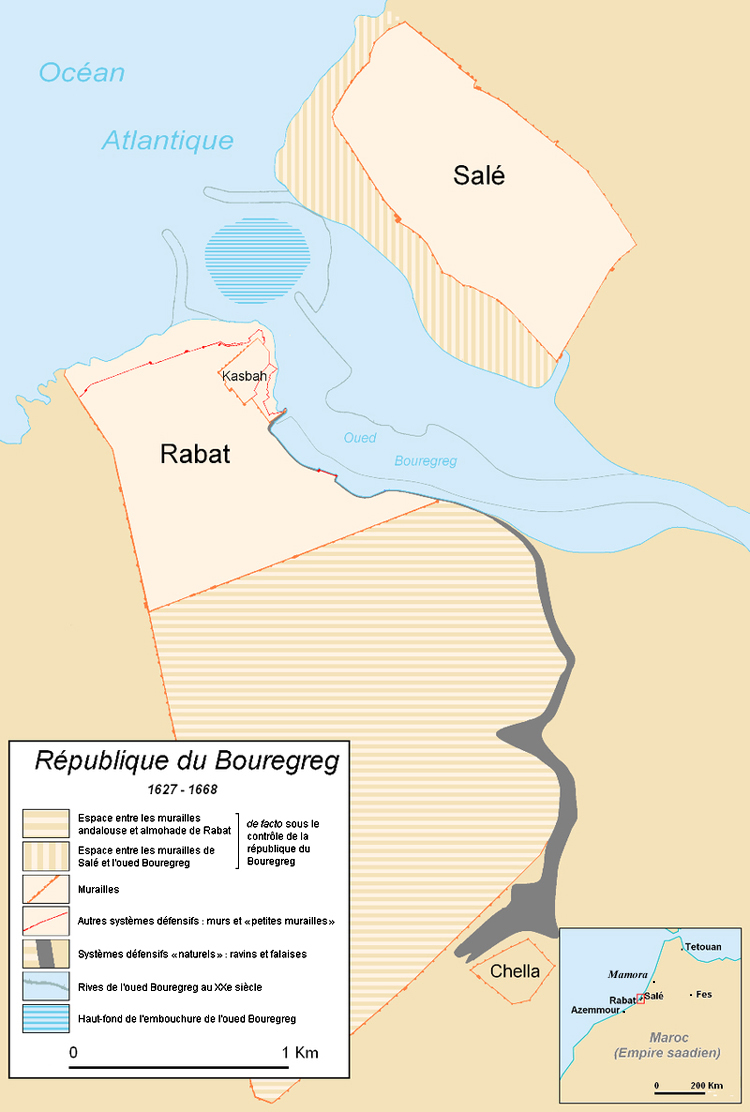
Salé Morisco Republic #1
Return
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Fasis | People of Fez |
| Makhzan | In Fez or at Marakesh, the central administration of the Moroccan Sultanate, composed of the governor, judge, market inspector, administrator of pious endowments, customs officers, etc. |
| Salā Colonia | Roman colony at Salā |
| Salāwis | People of Salé |
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| a'bd, abid | Slaves (ALL men are God's slaves, or God is the highest slave-master: Religion is based upon slavery) |
| a'yān | Notables, upper bourgeoisie, government officials, leading scholars, holy men, wealthy farmers, tanners, crftsmen, merchants |
| al-'āmma | Commoners or masses, middle petty bourgeoisie |
| al-'arab | Arab. |
| al-aṭrāf | Personages. |
| al-a'yān | Notables. |
| al-'āmma | Urban society (not riff-raff). |
|
al-'āmma al-aghmār,
ghawghā' l-ḥāḍira, ghawghā' 'l-'arab, 'āmma |
Ignorant masses,
urban rabble, rural rabble, the illiterate |
| al-bādiya | Rural way of life practiced by "Arabs" or "Bedouins". See al-ḥaḍāra. |
| al-barrāḥ | Town crier. |
| al-barrāniyīn | Outsiders, fishermen, hired workers, farm laborers, peddlers, domestics, slaves, lower proletariat |
| al-bawādī | Bedouin. |
| al-bilād | Townsmen, petty officials, shopkeepers, farmers, craftsmen, middle petty bourgeoisie |
| al-ḥaḍār | Urban way of life. See al-bādiya |
| al-ḥajjāmīn | Barbers |
| al-khāṣṣa, al-wujahā' | Elite, upper bourgeoisie, government officials, leading scholars, holy men, wealthy farmers, tanners, craftsmen, merchants |
|
al-mallāḥ, mellah,
al-mullāḥ, al-quadīm |
Jewish quarter (ghetto) |
| al-qaiṣariyya dhāt as-sawārī | Bazaar of Columns (retail sale of cloth and woollen goods) |
| al-qashshāshin | Felt hat makers |
| al-qā'a |
An important Salé caravansary (Funduk), the "Courtyard".
Goods sold: butter (fresh and clarified), honey, wool (raw), beef (dried), cumin, olives, figs, dates, raisins, walnuts, almonds, henna, kat. Notaries kept records. |
| 'arīqīn | Old, deep-rooted, respectable Salé families. |
| as-sammārīn | horseshoers |
| as-sifla | Riff-raff, lower proletariat. |
| as-suwayqa | Small market. |
| ash-shurafā' | Descendants of the Prophet. |
|
at-taqwīm al-hijrīy
(Salé Lunar Months) |
|
| at-tujjār | Merchants. |
|
awlād an-nās,
ahl l-bled |
Prominent families (the well born, literally sons of important people),
The (important) people of the city. |
|
bāb fās,
al-mullāḥ, al-quadīm,
bāb sibta, bāb al-jadīd |
Gate of Fez,
Gate of Ceuta, New Gate |
| dabbāgha | The suppliers of leather and of tanners in the late 19th century. Shoes were then made in Salé. |
| dār al-barūd | Storehouse for ammunition. |
| dhawū'l-buyūt | Men of known families. |
| Drūba | Streets of a neighbourhood. See tanāfus. |
| Funduq | Warehouse, hotel |
| Gharb | North |
| ḥaddādīn | Tinsmiths |
| ḥammāms | Public ovens, public baths, Quranic schools, shops |
| ḥanbals | Woollen rugs from Salé |
| Haouz | South |
| ḥassārīn | matmakers |
| ḥurma | An inviolable sanctuary (of a lodge). |
| ḥūma, ḥūmāt | Quarters or neighborhoods |
| Jnān | Unirrigated gardens (extensive in Salé). See sāniya. |
| Jōṭiyya | Flea Market. |
| kharrāza | Shoemakers (By the late 19th century, the shoemaking industry replaced weaving.) |
| kherba | A stable for riding animals or other animals (cows, sheep, goats). |
| l-qa'ida | The code of politness, discretion, propriety, decency, clenliness, ways of cooking, table manners, and rules of proper dress. |
| Madīna | Urban settlement or city: commercial sector as opposed to a residential sector and may contain a Jewish (bourgeois) gated ghetto, walled in, gate shut at night. |
| maḥāl al-ḥūt | Fish market. |
| majlis | Disciples of a religious teacher. |
| malḥūn | A poetical form using stylised form of the spoken language. |
| m'allim, ṣunnā' | Master craftsmen, apprenticed artisan journeymen (ahl al-ḥirāf): industry was organized as guilds (ḥnāṭ) in Salé during the 19th century. There were itinerant traders and shopkeepers (suwwāqa, sāḥāt al-aswāq wa-ahl al-ḥawānit). Guilds were led by a chief (l-amīn) with his assistant (khalīfa). |
| mitḥasib | Market provost |
| mizrag | Guarantee of safe passage for traders. |
| muḥtasib | Administrator to ulama official. |
| mujāhid&umacrn | Holy warriors. |
| qaiṣariyyat al-yahūd | Bazaar of the Jews. |
| qaiṣariyyat dhāt as sawārī | Bazaar of Columns (cloth and woolen goods) |
| qibla | Qibla is the direction to the Ka'ba in Mecca, used to determine directions to construct a house or the direction to turn at the time of prayer. |
| raḥbat az-zra' | Square for wheat. |
| riyāḍ | A fruit tree garden connected to by a passage (mduwwiz) through the house. |
| sāniya | Pivate irrigated gardens (or water scoops) in Salé where oranges, pomegranites, pears, apricots and lemons were grown. See jnān. |
| shahāda | Declaration of the belief of Islam: "There is but one God and Muhammad is the messenger of God." |
| shaykh | Leader of a religious order. |
| shurafā' | Leaders of the "descendants of the Prophet. |
| sība | Anarchy or opposition. |
| Siqqāya | Public wells. |
| Sulaḥā' | Pious men. |
| sūq | Market place. |
| sūq al-gazzārīn | Butcher market |
| sūq al-ghazl | Thread market. |
| sūq al-kabīr | Great Market Place. |
| tanāfus | Neighbourhood rivalry (especially by children). See drūba |
| 'ulamā' | Learned men. |
| Ūlād l-ḥrām | Those that cannot be married (illegitimates). Marriages between Muslims and Jews were inadmissible. |
| 'udūl | Notaries. |
| zāwiya | Hajjī Sufi lodge (see ḥurma) Most lodges had a separate room for prayer, with a mausoleum of a saint, covered with a qubba (dome) |
| zīt bildī | Warehouse for leather (fresh and dried tanners skins) and olive oil. |
© Copyright 2006 - 2019
The Esther M. Zimmer Lederberg Trust
 Website Terms of Use
Website Terms of Use